Modern applications don’t fail quietly—they generate signals. Logs, metrics, traces, and telemetry stream continuously, yet most enterprises still struggle to turn this data into decisions. Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL changes that equation by introducing a unified data access layer for Microsoft Fabric, allowing application telemetry, operational logs, and analytics data to be queried and visualized with precision and speed. For digital-first enterprises, this is not just another GraphQL API for Microsoft Fabric—it’s a new way to observe application behavior, monitor performance in real time, and expose actionable insights directly into Power BI dashboards. At DynaTech, we see this as a foundational capability for modern DevOps, SRE, and engineering-led organizations that want clarity, not complexity, from their data.
Why Unified Data Access Is the Missing Layer in Application Monitoring
Most applications are already instrumented. Telemetry flows from Azure Application Insights. Logs sit in Azure Log Analytics. Data exists, but insight doesn’t.
The gap is access.
Teams still query metrics and logs separately. Different tools. Different languages. Different outputs. By the time data is stitched together, the incident has already moved on.
Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL removes that friction.
It introduces a unified data access layer for Microsoft Fabric. It allows telemetry and log data to be queried together in a single request. No over-fetching. No duplicate APIs. Just the fields the application or dashboard actually needs.
For DevOps and IT leaders, this changes daily operations:
- Logs and telemetry become queryable assets and not raw exhaust
- Correlation happens at query time and not after incidents
- GraphQL for enterprise data enables faster root-cause analysis
- Power BI dashboards stay real-time and not reactive
Unlike rigid REST endpoints, the GraphQL API for Microsoft Fabric adapts to how teams think about problems. Ask one question. Get one response. Stream it into Power BI. Act.

What Is Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL?
Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL is a native data access layer. It allows applications and analytics tools to query Fabric data using GraphQL.
Instead of writing multiple SQL, KQL, or REST queries, teams expose selected Fabric data sources once and access them through a single GraphQL endpoint. The API automatically handles schema discovery, query generation, data resolution, etc. Modern apps consume data on demand and not in bulk. GraphQL enables this by returning only the required fields, precisely shaped for each use case.
Within Microsoft Fabric, the API can expose data from:
- Fabric Data Warehouses
- Fabric SQL Databases
- Lakehouses via SQL Analytics Endpoints
- Mirrored databases (Azure SQL, Azure Cosmos DB, Snowflake, Databricks)
This makes the Microsoft Fabric integration API especially powerful for operational monitoring scenarios. For enterprises standardizing on Fabric, this is not “another API.”
It is the unifying interface for Microsoft Fabric data access. It is built for scale and performance.
How Microsoft Fabric GraphQL API Fits into Developer Workflows
For developers, the Microsoft Fabric GraphQL API acts as a single and predictable data interface across OneLake, warehouses, and semantic models. Instead of stitching together REST endpoints or handling multiple query languages, developers work with one GraphQL schema. This schema reflects governed enterprise data.
This means faster app development and cleaner front-end queries, along with fewer backend transformations. All of this while still respecting Fabric security, permissions, and data models. The focus shifts from data plumbing to building features.
Microsoft Fabric GraphQL API: Developer Use Cases
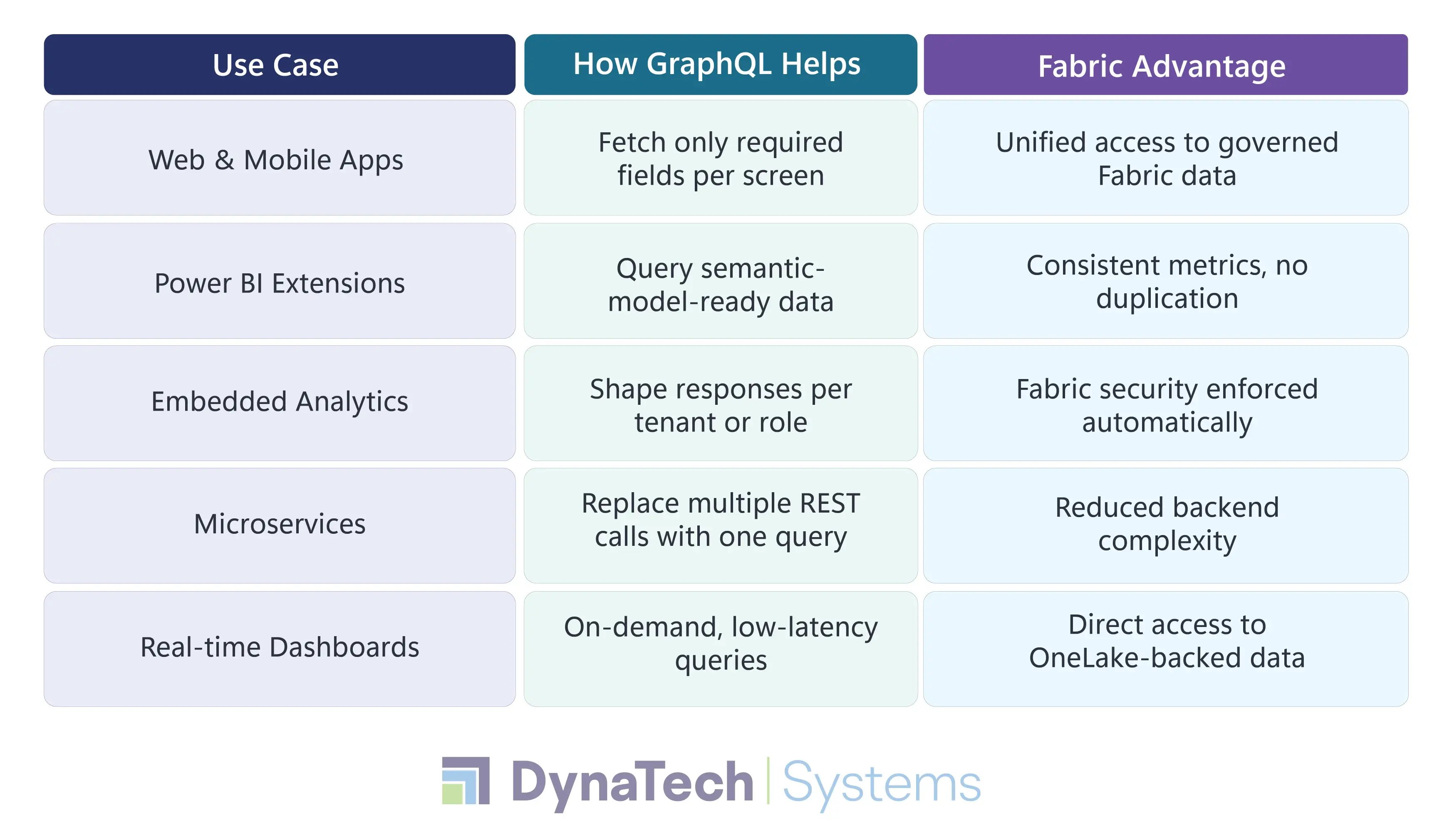
Microsoft Fabric GraphQL API — Feature Breakdown for Developers
The Fabric API for GraphQL is engineered to eliminate hand-built API layers. Instead of wiring schemas and access logic manually, Fabric automates the entire lifecycle.
Schema & API Generation
- Automatic discovery of schemas from connected data sources
- Auto-generated GraphQL queries and mutations
- Built-in resolver generation with no custom coding
- Local test code generated out of the box for faster validation
Data Source Coverage
- Native support for SQL views in databases and warehouses
- Execution support for stored procedures
- Single API layer spanning multiple data sources with fan-out queries
Data Modeling & Exposure Control
- Tools to define one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships
- Ability to expose only selected objects from a data source
- Column-level controls to restrict what fields are accessible
Observability & Governance
- Centralized dashboard to monitor API behavior
- Detailed request logging for debugging and performance analysis
The result is a production-ready GraphQL layer. It stays tightly aligned with Fabric data models, without introducing additional infrastructure or any kind of maintenance overhead.
Practical Use Cases: Where Microsoft Fabric GraphQL API Delivers Real Value
The Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL isn’t a theoretical layer. It is built for real application patterns that developers deal with every day.
- Web & Mobile Apps: Fetch only required fields per screen. This fastens load times and cleans frontend code.
- Live Dashboards: Enable near real-time analytics by exposing mirrored Cosmos DB data. This is done through GraphQL.
- Microservices & BFF: Use GraphQL as a flexible aggregation layer. It shapes data per client without an API sprawl.
- AI Agents: Expose Fabric data (Lakehouse, Warehouse, DBs) through a single interface for AI-driven apps.
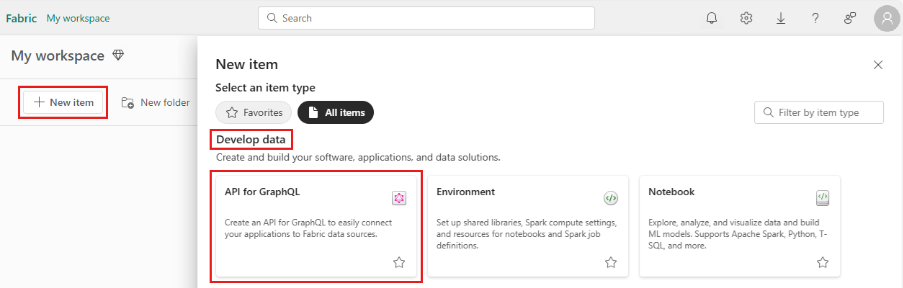
Create an API for GraphQL in Fabric
Select New item from any workspace. Under Develop data, choose API for GraphQL.
Enter a Name for your API and select Create.
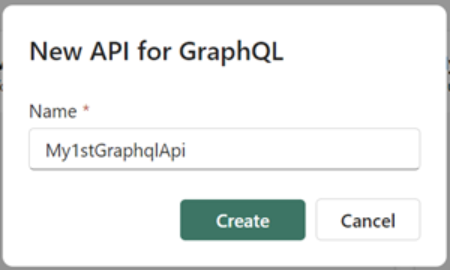
Your API is now created and ready to securely access data in Microsoft Fabric.
Connect to a data source and build your schema
1. In your new API, choose a data source to expose by choosing Select data source.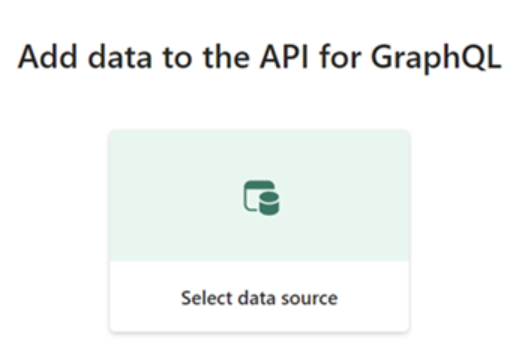
2. Next select the connectivity option for your API:
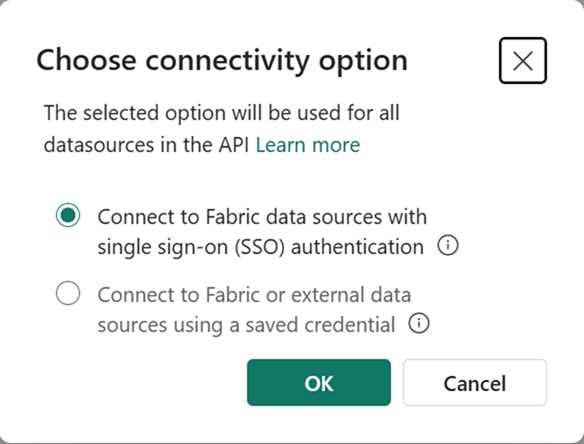
You can configure how API clients access the endpoint to execute GraphQL requests. They can choose between two distinct options:
3. The OneLake data hub appears. Choose the data source you want to connect to. In the following example, the user has selected an Adventure Works SQL analytics endpoint linked to a mirrored database.
Select Filter to see only specific types of Fabric data sources or search by a specific keyword. When you're ready, select Connect.
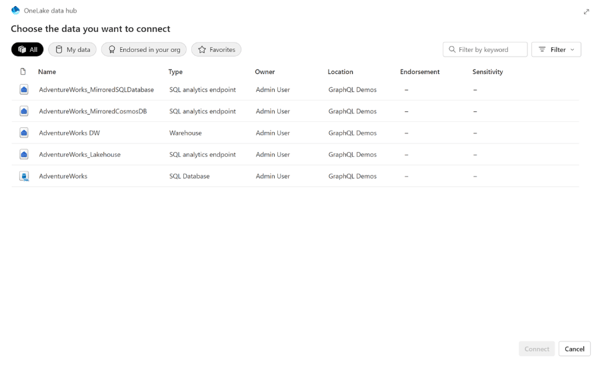
4. The Get data screen appears. Here, you can choose which objects you want exposed in your GraphQL schema.

5. Select the checkboxes next to the individual tables, views, or stored procedures you want to expose in the API. To select all the objects in a folder, select the checkbox with the data source name at the top.
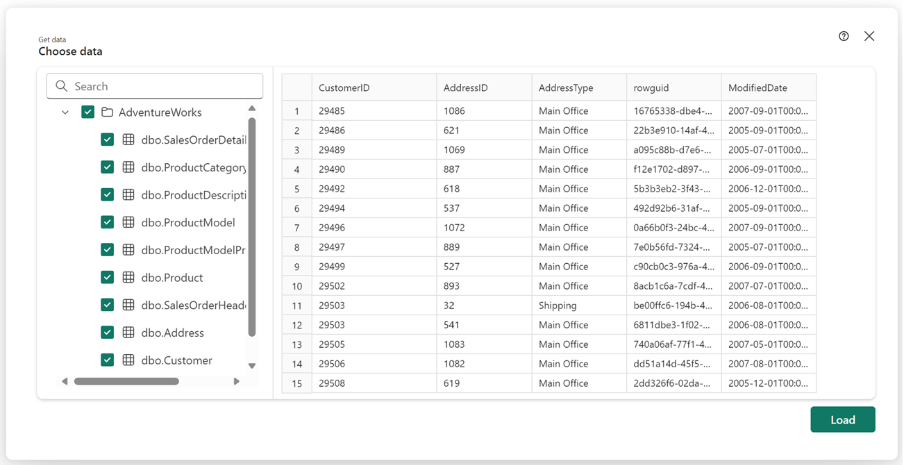
6. Select Load to start the GraphQL schema generation process.
7. The schema is generated. Now, you can start prototyping GraphQL queries (read, list) or mutations (create, update, delete) to interact with your data.
Conclusion
Accessing the right data quickly is a constant challenge for many organizations. The Microsoft Fabric API for GraphQL solves this problem. It unites telemetry, logs, and analytics into one simple interface. It cuts through the noise. Hence, teams can focus on what matters. They can make faster and smarter decisions.
At DynaTech, as a Microsoft Solutions Partner, we understand the power of streamlined data access. We build tailored solutions that help businesses turn complex data into clear insights. Our expertise ensures you get more value and less hassle.
If you’re ready to move beyond fragmented data and truly harness the capabilities of Microsoft Fabric, connect with us. Let’s help you unlock the full potential of your data and drive meaningful results.